Product Introduction
Types of UV Laser Marking Machines
-

FM-UD Laser Marking Machine
Rated 4.75 out of 5$5,070.00 – $12,090.00Price range: $5,070.00 through $12,090.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
FM-UH Laser Marking Machine
Rated 4.50 out of 5$5,460.00 – $12,480.00Price range: $5,460.00 through $12,480.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

FM-US Laser Marking Machine
Rated 4.75 out of 5$5,200.00 – $12,220.00Price range: $5,200.00 through $12,220.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

FM-UP Laser Marking Machine
Rated 4.75 out of 5$5,330.00 – $12,350.00Price range: $5,330.00 through $12,350.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

FM-UE Laser Marking Machine
Rated 4.88 out of 5$6,370.00 – $13,390.00Price range: $6,370.00 through $13,390.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

FM-UF Laser Marking Machine
Rated 4.50 out of 5$7,150.00 – $14,170.00Price range: $7,150.00 through $14,170.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Application of UV Laser Marking Machines




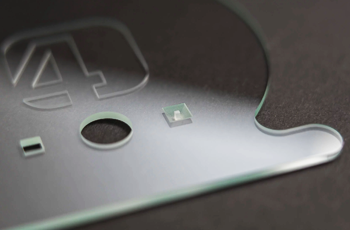
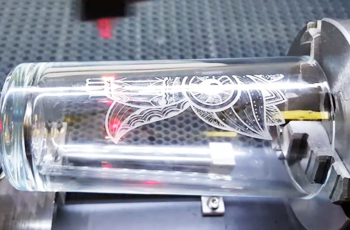

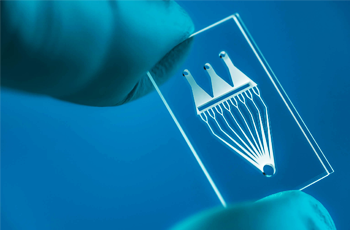
Why Choose Us
Precision Engineering
Our machines deliver ultra-fine marking and engraving with high-speed galvanometer systems and stable laser sources for consistent, reliable output.
Wide Material Compatibility
We offer different laser types to match your needs, ensuring crisp, permanent marks on metal, plastic, wood, leather, and more.
User-Friendly Software
Intuitive control software allows easy setup, flexible design import, and precise marking even for first-time users.
Customizable Solutions
We provide machine options tailored to your product size, line speed, and marking content for seamless integration.
Low Maintenance
Our systems run cleanly with no inks or chemicals, lowering long-term operating costs and environmental impact.
Dedicated Support and Service
Faster Laser offers professional training, remote troubleshooting, and responsive service to keep your production running smoothly.
UV Laser Marking Machines VS Other Marking Machines
| Feature / Machine Type | UV Laser Marking Machine | Dot Peen Marking Machine | Inkjet Printing Machine | Stamping Machine |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marking Method | Ultraviolet laser (cold marking) | Mechanical pin striking | Ink sprayed onto surface | Die pressed into material |
| Wavelength | 355 nm (short, high-precision beam) | Not applicable | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| Heat Impact | Very low (ideal for heat-sensitive materials) | None | None | High (due to force) |
| Marking Precision | Extremely high (micro-text, fine detail) | Moderate | Moderate | Low to moderate |
| Material Compatibility | Plastics, glass, ceramics, films, semiconductors | Mostly metals | Paper, cardboard, plastics | Metals and rigid materials |
| Suitable for Transparent Materials | Yes | No | No | No |
| Contact or Non-Contact | Non-contact | Contact-based | Non-contact | Contact-based |
| Marking Durability | Permanent, non-destructive | Permanent | Temporary (can smear or fade) | Permanent |
| Maintenance Requirements | Low (no consumables) | Moderate (mechanical parts) | High (ink and nozzle cleaning) | High (die wear and maintenance) |
| Environmental Impact | Minimal (no chemicals or ink) | Low | High (ink waste and VOCs) | Moderate |
| Setup Time | Short | Moderate | Short | Long (requires custom dies) |
| Operating Cost | Low (no ink or consumables) | Low | High (ink, solvents, maintenance) | Moderate (tooling and labor) |
| Noise Level | Low | High | Low | High |
| Automation Compatibility | Excellent (inline, robotic systems) | Limited | Good | Limited |
| Common Applications | Electronics, medical, plastics, glass, semiconductors | Metal parts, nameplates, tools | Packaging, date codes, labels | Coins, logos, heavy parts |
Customer Testimonials
Related Resources

Laser Marking VS Screen Printing
This article explores the key differences between laser marking and screen printing, comparing their processes, advantages, disadvantages, applications, and how to choose the right method for your needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is UV Laser Marking?
- Minimal Thermal Damage: Since UV lasers operate with low heat, they avoid charring, melting, or deforming materials—ideal for plastics, glass, and thin films.
- Extremely Fine Marking: The short wavelength enables micro-marking down to micrometer-scale detail, perfect for small components and sensitive substrates.
- High Contrast and Accuracy: Produces clear, readable text and barcodes even on transparent, dark, or multi-layered surfaces.
What Laser Power Options Are Available For UV Laser Marking Machines?
- 3W UV Lasers: Best for micro-marking and applications requiring ultra-low thermal impact. The 3W UV laser is ideal for fine detail on plastics, films, and delicate electronic components where material distortion must be avoided.
- 5W UV Lasers: A versatile mid-range option for marking a wide variety of non-metallic materials, including packaging, labels, and coated glass. This power level offers a balance between precision and marking speed, making it suitable for both industrial and commercial use.
- 10W UV Lasers: Better suited for higher throughput environments. This power level supports faster marking on slightly harder materials or deeper contrast marks on plastics and coated surfaces. It is commonly used in the electronics, automotive, and pharmaceutical industries.
- 12W UV Lasers: Offers greater marking efficiency while maintaining the UV laser’s inherent advantage of low heat. The 12W configuration is used for batch processing, high-speed conveyor integration, and marking on heat-sensitive plastics in high-production environments.
- 15W UV Lasers: The highest standard power option for UV systems, the 15W laser is used for fast, continuous operation with deeper penetration and broader coverage. It is ideal for industries requiring rapid marking on plastic enclosures, PCBs, and anti-counterfeit coding on coated substrates.
What Is The Price Of UV Laser Marking Machines?
- Plastics and Polymers: UV lasers mark a wide variety of plastics without melting or charring, producing high-contrast, crisp results.
- ABS, PVC, PE, PET, PEEK: Common in electronics, medical devices, and packaging.
- Polycarbonate and Acrylic (PMMA): UV lasers avoid yellowing or edge burn.
- Coated Plastics and Laminates: Perfect for consumer products and decorative parts.
- Glass and Ceramics (Engraving Only): UV lasers do not cut through these materials, but they can etch or engrave surfaces precisely.
- Clear and Colored Glass: Used for decorative marks, serial numbers, or branding.
- Ceramic Tiles or Components: Suitable for electronics and consumer goods.
- No micro-cracking or stress is introduced if processed properly.
- Films, Foils, and Thin Coatings: The low heat of UV lasers makes them excellent for thin or multi-layer materials.
- Packaging Films (BOPP, PET film): UV can code expiration dates or batch info.
- Holographic Foils and Labels: Precise surface marking without peeling or distortion.
- PCB Solder Masks: UV lasers are used to engrave marks directly onto boards.
- Metals (With Coating or Surface Treatment): Though UV lasers cannot deeply engrave bare metal, they can mark on:
- Anodized Aluminum and Coated Stainless Steel: Producing fine, contrast-rich marks.
- Electroplated or Painted Metals: No damage to the base layer.
- Gold and Silver (limited): Surface marks only, with low reflectivity.
- Semiconductors and Silicon Wafers: UV laser marking is frequently used in the microelectronics industry to mark components without thermal damage.
- Silicon chips, transistors, sensors: Ideal for marking tight spaces with micron-level accuracy.
- Photovoltaic Cells: Code and track without affecting function.
What Materials Can Be Marked With UV Lasers?
- Plastics and Polymers: UV lasers mark most plastics without melting, burning, or warping, delivering high contrast and precision.
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): Crisp black or white marks without surface distortion.
- PE (Polyethylene) and PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate): Used in packaging, medical tubing, and bottles.
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): Marked without releasing dangerous fumes when done with proper ventilation.
- PC (Polycarbonate): No yellowing or deformation.
- PA (Nylon), PEEK, and other engineering plastics: High-clarity marking for industrial use.
- Glass and Ceramics (Engraving Only): UV lasers don’t cut through these materials but can produce fine, clean engravings on the surface.
- Glass (Clear, Colored, Coated): Bottles, touchscreens, labware, and ornaments.
- Ceramic Components: Tiles, insulators, medical implants, and electronics.
- Films, Foils, and Coated Materials: The low heat output makes UV lasers suitable for marking thin or multilayered surfaces.
- Food and pharmaceutical packaging films: Date codes, batch numbers, and logos.
- Holographic labels, anodized foil, and tamper-evident stickers: Marked without peeling or bubbling.
- PCB solder masks and flexible electronics: High-precision marking with zero delamination.
- Metals (With Coating or Surface Treatment): UV lasers are not ideal for marking bare metals, but they perform well on coated or treated metals.
- Anodized Aluminum: High contrast, non-destructive marking.
- Painted or Plated Metals: Surface marking without burning through the coating.
- Electroplated Steel or Stainless Steel: Precise text, logos, or traceability codes.
- Semiconductors and Silicon Wafers: UV laser marking is widely used in the electronics and semiconductor industry.
- Silicon, Gallium Arsenide, and other substrates: Marked for identification without damaging circuits.
- IC chips, MEMS devices, and solar cells: Excellent resolution and reliability.
What File Formats Do UV Laser Marking Machines Support?
- Vector Graphics (for logos, outlines, shapes)
- DXF (.dxf): Widely used CAD format; ideal for technical drawings and mechanical parts.
- PLT (.plt): Plotter format used for vector-based marking; compatible with CorelDRAW.
- AI (.ai): Adobe Illustrator files, often imported via conversion to PLT or DXF.
- SVG (.svg): Scalable Vector Graphics; great for crisp logos and web-exported designs.
- EPS (.eps): High-quality vector graphics for complex artwork.
- Raster Images (for photos and textured patterns)
- BMP (.bmp): Preferred format for laser-engraved grayscale images.
- JPG / JPEG (.jpg): Common image type, usually converted to bitmap during processing.
- PNG (.png): Useful for logos with transparent backgrounds.
- GIF (.gif): Supported for basic image engraving; less commonly used due to limited resolution.
- Text and Variable Data (for serial numbers, dates, batch codes)
- TXT (.txt): Simple text files used for direct engraving or automated data loading.
- CSV (.csv): Excel-style data sheets; ideal for variable data like product IDs or QR codes.
- XLS / XLSX (.xls, .xlsx): Excel spreadsheets for bulk marking tasks with multiple fields.
What Are The Disadvantages Of UV Laser Marking Machines?
- Higher Cost: UV lasers typically cost more than CO₂ or fiber lasers, with prices ranging from $5,500 to $20,000. This is due to the advanced laser source, complex optical systems, and niche applications. For businesses needing only basic marking on metals or wood, a fiber or CO₂ laser may be more economical.
- Lower Power Output: UV laser marking machines generally operate between 3W and 15W, which is much lower than fiber lasers. This limits their marking speed and depth, making them unsuitable for high-speed, high-volume industrial tasks or deep engraving on hard materials.
- Limited to Surface Marking: UV lasers are designed for surface-level precision and cannot cut materials or engrave deeply. If the job requires cutting or etching into metal, another laser type will be more appropriate.
- Not Ideal for Bare Metal: While UV lasers can mark coated or anodized metals, they are not effective on bare or reflective metals such as stainless steel or aluminum. Fiber lasers are far superior for these materials.
- Maintenance Sensitivity: UV laser systems have sensitive optical components that require a clean, temperature-controlled environment. Dust or misalignment can easily reduce performance. Regular cleaning, calibration, and cooling are necessary for optimal results.
- Small Marking Field: Most UV systems offer smaller marking areas (e.g., 110×110 mm or 150×150 mm) due to the nature of the optics. For larger items or batch engraving, this can limit productivity and require frequent repositioning.
What Are The Cooling Methods For UV Laser Marking Machines?
- Air Cooling: For low-power models such as 3W and some 5W UV laser marking machines, air cooling is commonly used. These systems rely on internal fans and heat sinks to dissipate heat generated during operation. Air-cooled UV lasers are compact, energy-efficient, and easy to maintain, making them ideal for small-scale applications like electronics marking, packaging labels, and fine-detail engraving on plastics. Because they generate less heat, these systems can operate efficiently without the need for external cooling units, making them a cost-effective choice for workshops with limited space or lower production demands.
- Water Cooling: UV laser systems with 5W (used in continuous-duty settings), 10W, 12W, and 15W outputs generate more heat and require a more robust thermal management system. Water cooling systems work by circulating chilled water through a closed loop around the laser source, efficiently removing heat and ensuring the machine maintains a consistent operating temperature. This cooling method is critical for high-speed, long-duration, or batch production applications where performance stability and long-term reliability are key.
How To Maintain UV Laser Marking Machines?
- Optical Components: UV lasers operate using high-precision optics, including lenses and mirrors. Dust, oil, or residue buildup can interfere with the laser path and reduce marking quality. Clean the f-theta lens and galvo mirrors regularly using lens-grade wipes and isopropyl alcohol. Always avoid direct contact with fingers and ensure the environment is as dust-free as possible.
- Cooling Systems: UV laser marking machines rely on effective cooling to prevent overheating, especially during prolonged use. Air-cooled systems, typically used in 3W or 5W models, require regular inspection of fan vents and filters. Water-cooled systems, common in 10W to 15W models, must be flushed periodically. Replace the distilled water every 3-6 months, clean the chiller, and check for leaks or clogs in the tubing.
- Work Area and Enclosure: The interior of the machine and the surrounding work environment should be kept clean. Material residue and vaporized particles can accumulate on the lens and internal components. If your machine uses a fume extractor, change the filters according to the manufacturer’s guidelines to maintain safe and efficient operation.
- Software and Firmware: Keep the marking software (such as EZCAD) updated to access the latest features and ensure compatibility. Back up all configurations and parameter settings before performing any software updates. Periodically check communication between the PC and the controller to prevent data transfer issues.
- Electrical and Mechanical Checks: Inspect the power supply cables, connectors, and ground wires for signs of wear or looseness. Tighten connections and ensure stable voltage input. If your machine includes a motorized z-axis or rotary device, lubricate rails and moving parts as specified in the user manual.
- Laser Output Monitoring: Over time, the laser’s output power may degrade. Using a power meter, check that the UV laser still emits within the expected range. A noticeable drop in marking contrast or depth may indicate that recalibration or source replacement is necessary.
- Routine Preventive Maintenance: Conduct a full inspection every 3 to 6 months. This should include optics cleaning, alignment verification, cooling system service, software checks, and performance benchmarking. Keep a maintenance log to track service history and detect recurring issues early.
